A lot of our users complain about their internet connection being slow. One possible boost for your connection is a Windows technology called DCA if you have an old CPU
First Things First: Try Simpler Approach!
Before enabling DCA, you should make sure to follow our general guides first. Changing your DNS provider can help most of you out there to speed up your connection, because OpenDNS and GoogleDNS are incredibly fast, while your provider may not be so great.
Here’s a great guide to change the DNS provider on Windows 8
If your browser is ok but your game experience (latency) is not so great, then you may also want to apply this useful tweak
What Is DCA And Why You May Not Need It
DCA – short for Direct Cache Access – can improve your connection by transferring data directly to your CPU cache. However, only certain motherboards actually support DCA, so Windows disables DCA by default
According to this article, DCA is mostly effective for speeding up old CPU’s, so if you already have a good CPU this won’t do the trick for you and you should first try other things like changing your DNS, resetting your router and temporarily uninstalling firewalls and anti-virus software known for messing with your internet connection speed
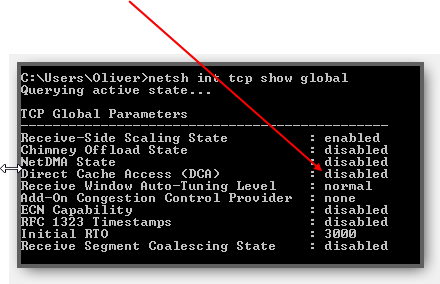
2 Check If DCA Is Disabled
We should first check the current state
1. Step Open a command prompt
2. Step Enter netsh int tcp show global and hit Enter
3. Step Enter netsh int tcp set global dca=enabled and hit Enter to enable DCA, should look like this:
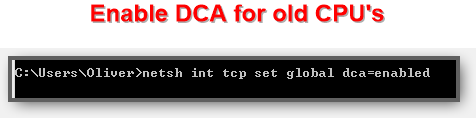
4. Step You will receive a message “Ok.”
5. Step Hit the “arrow up” twice to go back to the command we entered initially in step 2 and hit Enter again to see if DCA is enabled. It will still be disabled
6. Step Reboot your PC
7. Step Follow steps 1-3 again and it should now be enabled
Next Up: NetDMA
The NetDMA term was coined by the networking team to imply a DMA (Direct Memory Access) engine that is used for moving networking data in memory. During WinHEC I will present the NetDMA architecture but for now I will give you the problem that NetDMA is trying to address.
In part 2 we will enable NetDMA and talk a little about the TCP protocol.

